本文内容速览:
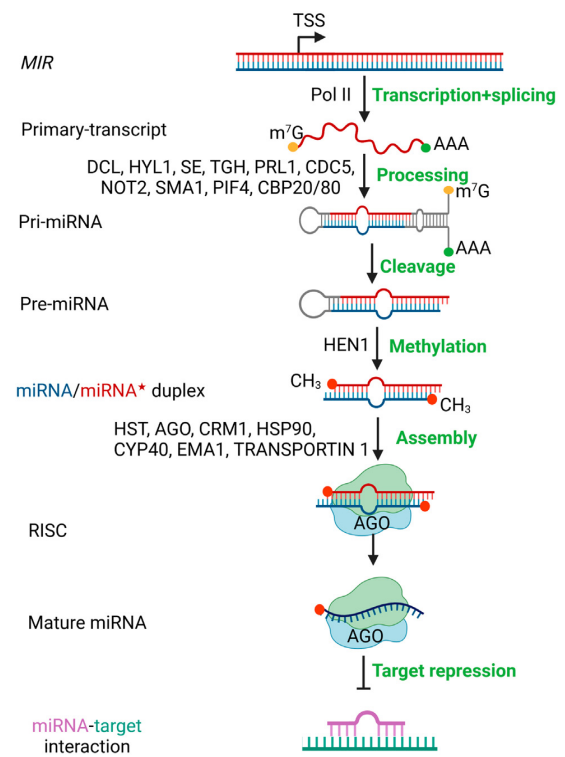
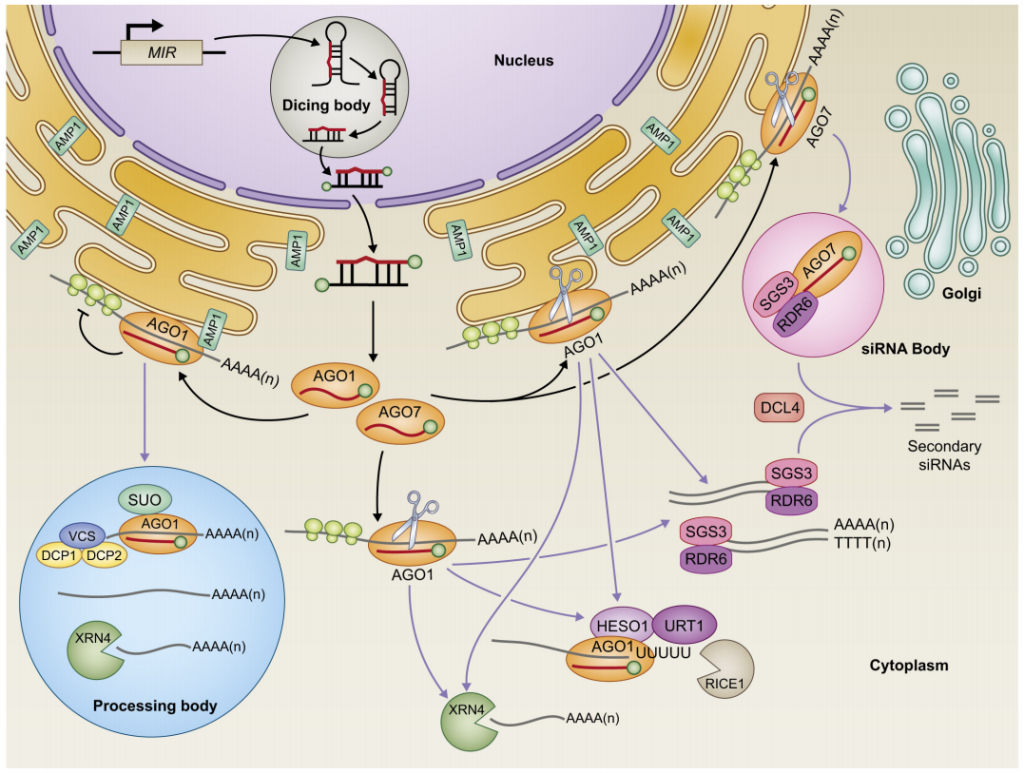
由于植物蛋白抗体开发不足,限制了对miRNA靶基因蛋白水平的检测,加之miRNA对靶基因mRNA剪切的研究被大量报道,在很长一段时间内,研究人员都认为植物miRNA主要通过剪切靶基因mRNA发挥作用。随着越来越多的研究表明有的植物miRNA并不影响靶基因mRNA的水平,而是降低靶基因蛋白的水平,由此提出植物miRNA也存在与动物miRNA类似的抑制蛋白翻译的作用。其大致机制是,成熟的miRNA与AGO1等相关功能蛋白结合后形成复合体,借助内质网上的ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM 1(AMP1)等蛋白定位到正在翻译的靶基因mRNA上,阻止核糖体的组装及翻译,不过该机制还需要更加深入的研究(张翠桔等,2020)。
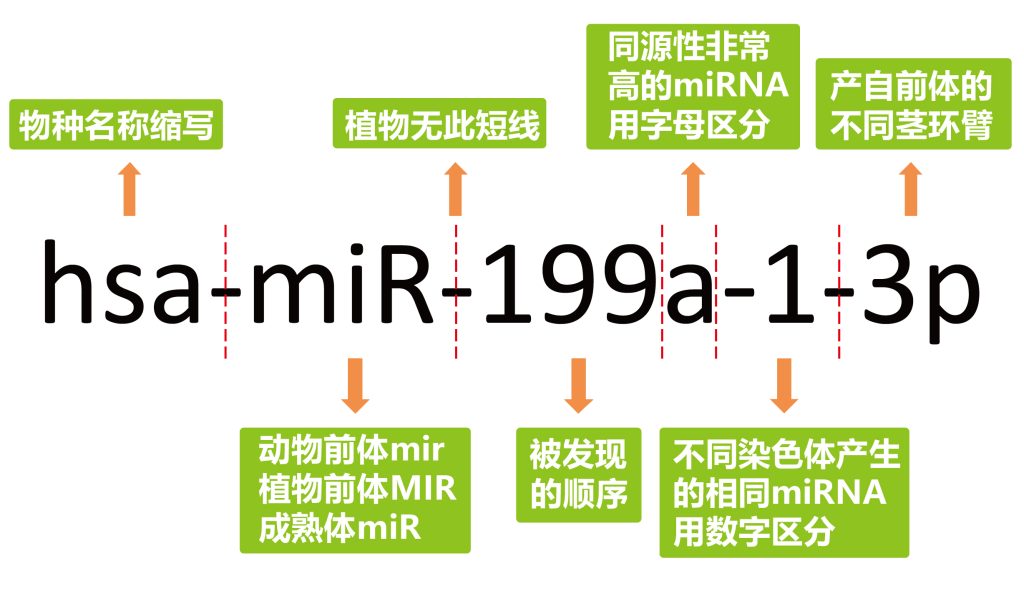
除了被miRNA的命名搞得一头雾水外,大家是不是也曾分不清siRNA、shRNA和miRNA,尤其是siRNA和miRNA,因为它们有许多相同之处,对于刚接触miRNA研究的小伙伴来说,很容易把它们混为一谈,关于这三种RNA的详细介绍,大家可以查阅小远的往期文章“siRNA、shRNA和miRNA,还在傻傻分不清?”进行学习哦。
在此推荐几个寻找miRNA前体序列的网站:
(1)miRBase:
http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk;
(2)PmiRKB:
PmiRKB Homepage (zju.edu.cn);
(3)RNAcentral:
https://rnacentral.org/search?q=sbi-MIR156d。
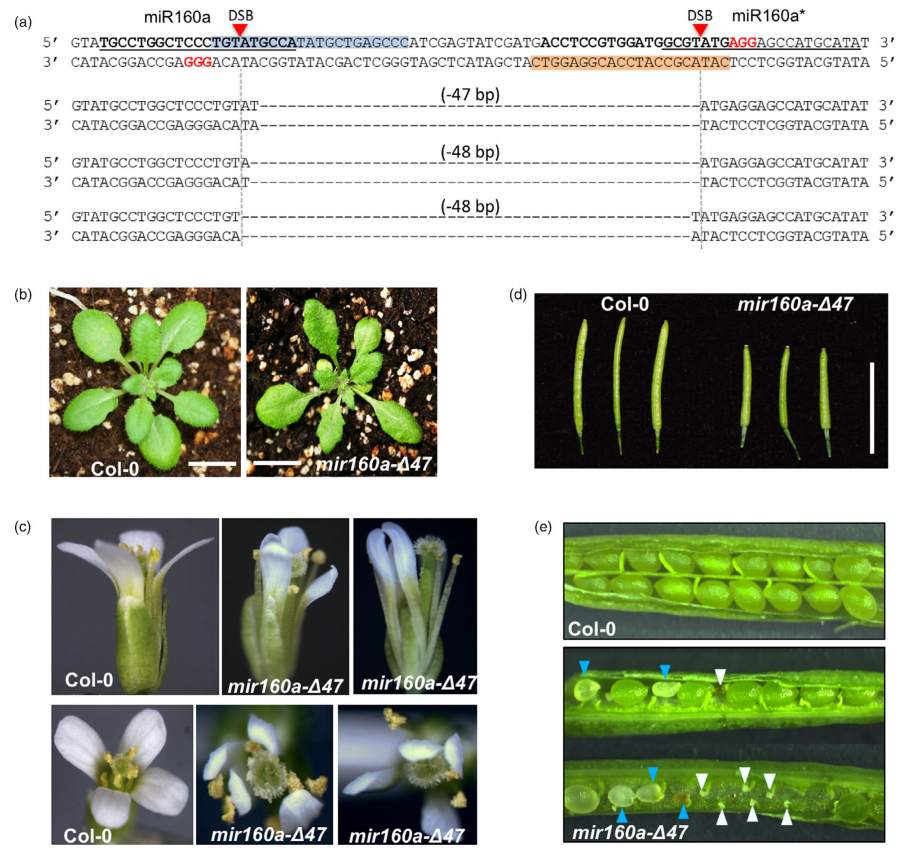
2020年7月,Bi等人在Plant Biotechnology Journal杂志上发表了一篇题为“Disruption of miRNA sequences by TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 induces varied lengths of miRNA production”的研究论文。在该论文中作者利用CRISPR/Cas9技术对拟南芥的MIR160a进行了基因编辑,通过在miR160a和miR160a*链上分别设计gRNA,并构建含有这两个gRNA的载体,结合遗传转化最终成功获得了大片段缺失的突变体(图8)。
(1)psRNATarget:
http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/
(2)TAPIR:
http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/tapir/
(3)miRdeepFinder:
http://www.leonxie.com/DeepFinder.php
(4)psRobot:
http://omicslab.genetics.ac.cn/psRobot/index.php
(5)WMD3:
http://wmd3.wei gelworld.org/cgi-bin/webapp.cgi
需要注意的是通过生物信息学预测的靶基因存在一定的假阳性,miRNA是否可以靶向剪切或抑制靶基因的表达最终仍需要采用生物学实验进行验证哦。
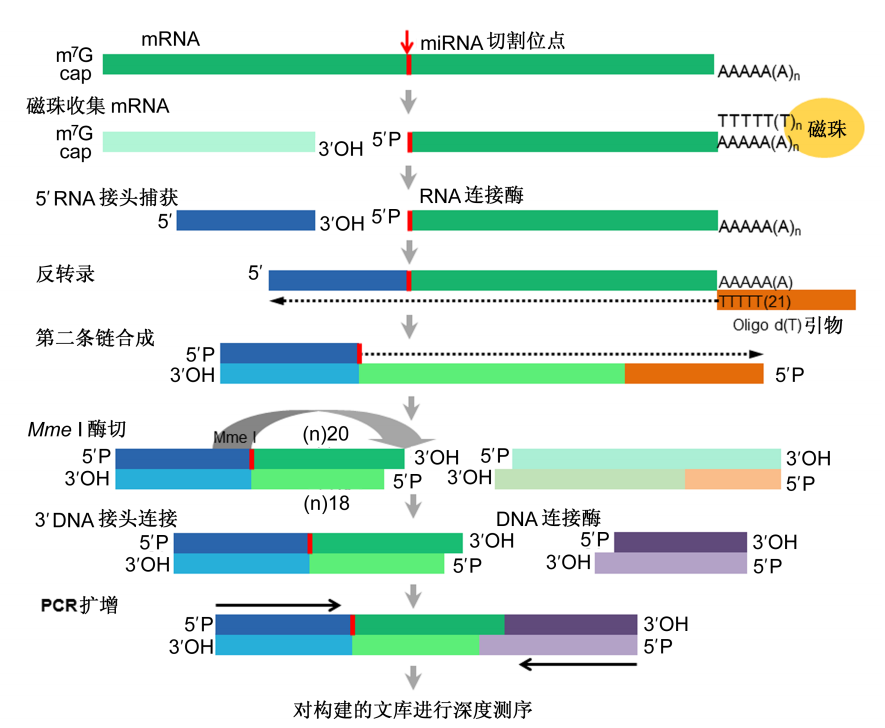
利用降解组测序,大家可以通过实验来寻找miRNA的靶基因,使得数据的准确性和说服力大幅提高,因而该技术也成为了miRNA靶基因鉴定的一大利器,不过该技术不能检测通过影响翻译抑制靶基因表达的miRNA。
因为没有检索到比较合适的文章,小远在此只列举一个利用RT-qPCR验证miRNA靶基因的案例,大家如果对蛋白免疫印迹比较感兴趣的话,可以自行查阅文献,也欢迎大家把文献分享给小远!
References:
Barik S, Kumar A, Sarkar Das S, et al. Coevolution pattern and functional conservation or divergence of miR167s and their targets across diverse plant species[J]. Scientific reports, 2015, 5(1): 14611.
Bi H, Fei Q, Li R, et al. Disruption of miRNA sequences by TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 induces varied lengths of miRNA production[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(7): 1526-1536.
Deng F, Zeng F, Shen Q, et al. Molecular evolution and functional modification of plant miRNAs with CRISPR[J]. Trends in plant science, 2022, 27(9): 890-907.
German M A, Pillay M, Jeong D H, et al. Global identification of microRNA-target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends[J]. Nature biotechnology, 2008, 26(8): 941-946.
Guo D L, Li Q, Lv W Q, et al. MicroRNA profiling analysis of developing berries for ‘Kyoho’and its early-ripening mutant during berry ripening[J]. BMC plant biology, 2018, 18(1): 1-16.
Kinoshita N, Wang H, Kasahara H, et al. IAA-Ala Resistant3, an evolutionarily conserved target of miR167, mediates Arabidopsis root architecture changes during high osmotic stress[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(9): 3590-3602.
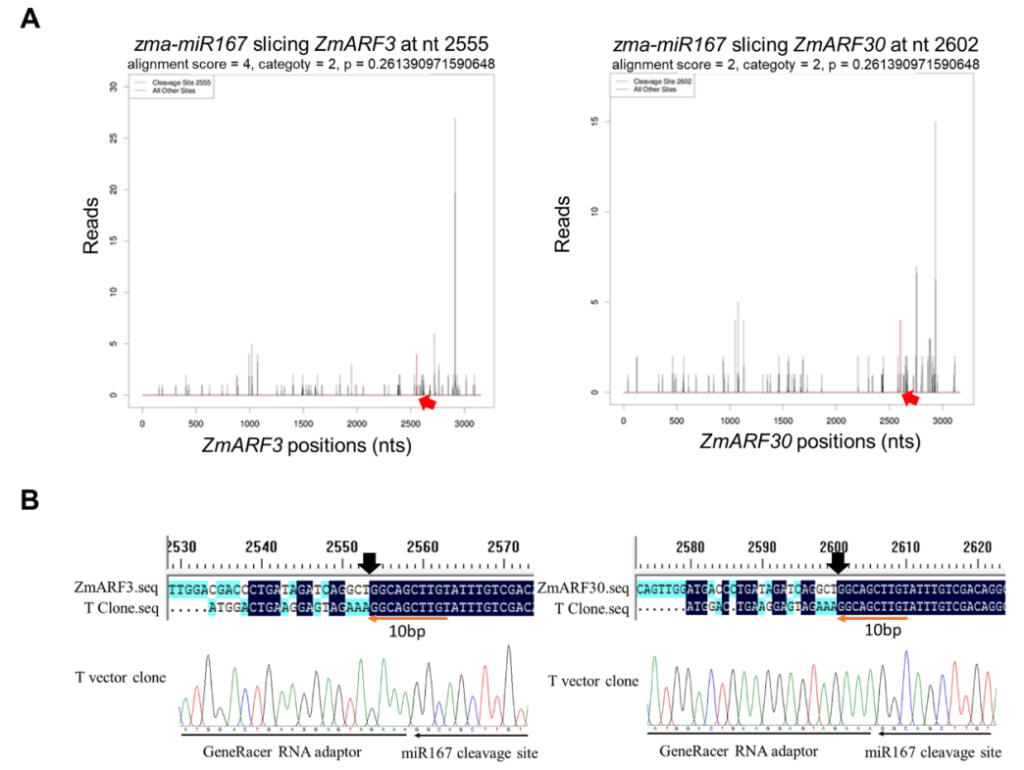
Liu X, Liu S, Chen X, et al. Maize miR167-ARF3/30-polyamine oxidase 1 module-regulated H2O2 production confers resistance to maize chlorotic mottle virus[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 189(2): 1065-1082.
Na G N, Mu X, Grabowski P, et al. Enhancing micro RNA 167A expression in seed decreases the α‐linolenic acid content and increases seed size in Camelina sativa[J]. The Plant Journal, 2019, 98(2): 346-358.
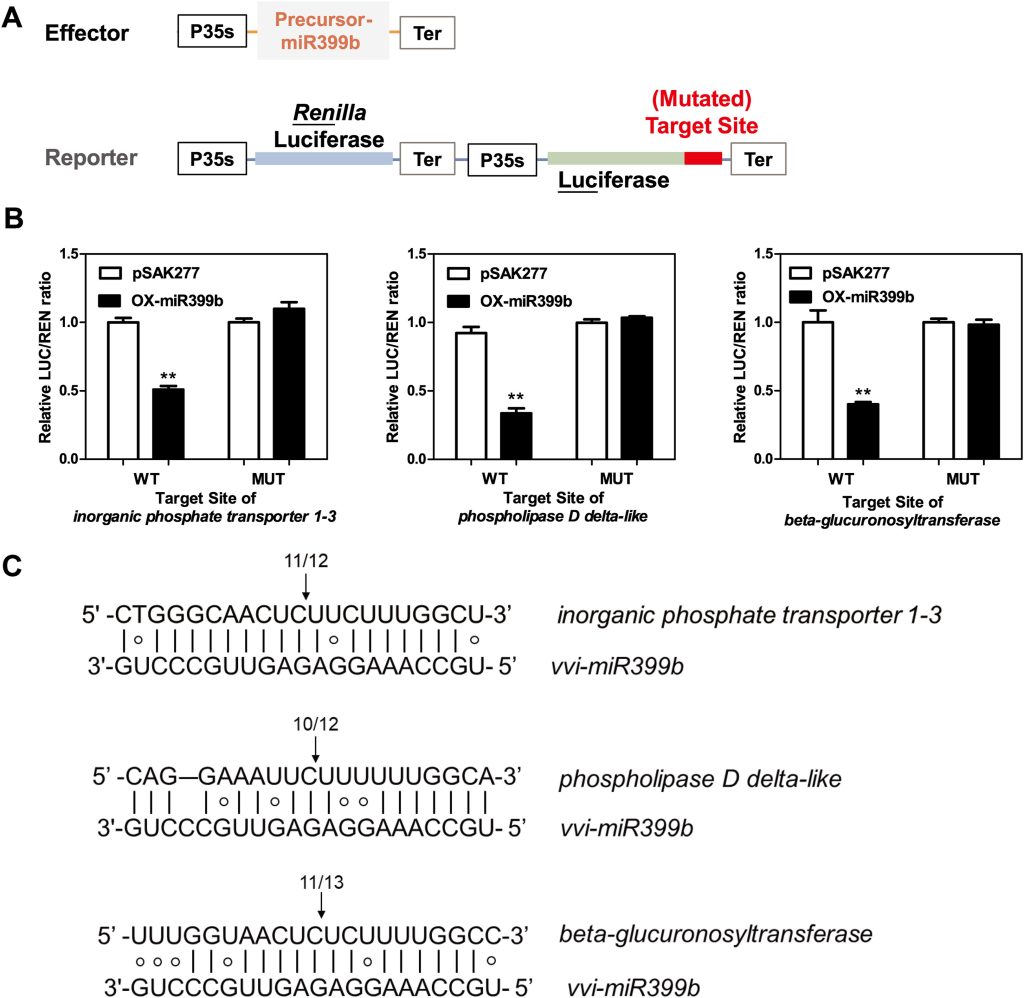
Pei M, Liu H, Wei T, et al. Identification, characterization, and verification of miR399 target gene in grape[J]. Horticultural Plant Journal, 2023.
Song X, Li Y, Cao X, et al. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plant–environment interactions[J]. Annual review of plant biology, 2019, 70: 489-525.
Varaud E, Brioudes F, Szecsi J, et al. AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR8 regulates Arabidopsis petal growth by interacting with the bHLH transcription factor BIGPETALp[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(3): 973-983.
Wang Y, Li K, Chen L, et al. MicroRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors GmARF8a and GmARF8b is required for soybean nodulation and lateral root development[J]. Plant physiology, 2015, 168(3): 984-999.
Wang L, Zhang W, Shen W, et al. Integrated transcriptome and microRNA sequencing analyses reveal gene responses in poplar leaves infected by the novel pathogen bean common mosaic virus (BCMV)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1163232.
Xu W B, Zhao L, Liu P, et al. Intronic microRNA‐directed regulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species enhances plant stress tolerance in Arabidopsis[J]. New Phytologist, 2023, 240(2): 710-726.
Yu Y, Jia T, Chen X. The ‘how’and ‘where’of plant microRNAs[J]. New Phytologist, 2017, 216(4): 1002-1017.
Yao X, Chen J, Zhou J, et al. An essential role for miRNA167 in maternal control of embryonic and seed development[J]. Plant physiology, 2019, 180(1): 453-464.
董淼, 黄越, 陈文铎等. 降解组测序技术在植物miRNA研究中的应用[J].植物学报, 2013, 48(03): 344-353.
张翠桔, 莫蓓莘, 陈雪梅等. 植物miRNA作用方式的分子机制研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(07): 1-14.